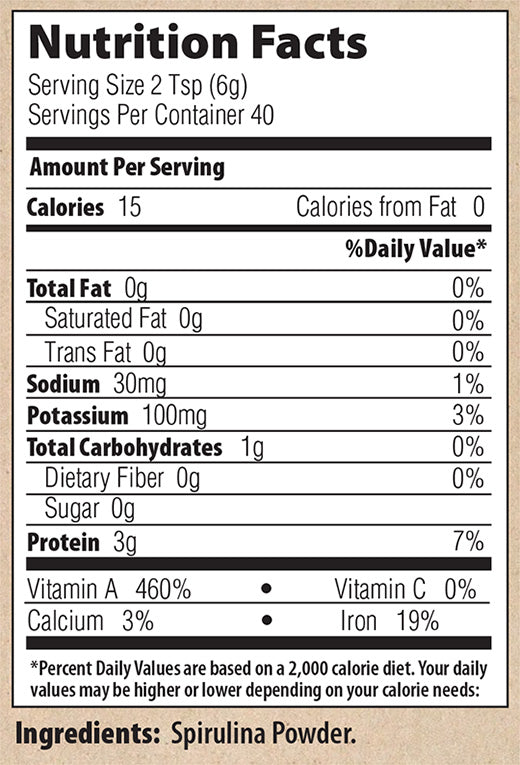
Spirulina, Arthrospira platensis, is a blue-green algae that has been cultivated and used as a complete food for thousands of years. In the Aztec culture it was called “Tecuitlatl” and was produced, collected and sold dried in cakes. The protein in spirulina is unusual for a plant-based source as it is “complete”. That means it contains all of the “essential” amino acids, those that our body cannot manufacture and must be consumed in food. It contains abundant amounts of many vitamins and minerals. For example it contains about 2.5 times the % daily value of vitamin A and a significant amount of iron. Because this iron is in an highly bioavailable form Spirulina is an excellent food to use to ensure adequate iron intake, especially for vegans.
Spirulina is grown in ponds, then collected and dried. No other processing is necessary. Spirulina is almost 50% by weight as protein so you can view it as a natural, nutrient enhanced protein powder and use it accordingly. It mixes best with fruit and particularly vegetables in smoothies or whole juices where the slightly vegetal taste is less evident. An important component of spirulina is called phycocyanobilin. It’s quite abundant and makes up about 1% of spirulina. Phycocyanobilin compound appears to act like the body’s own compound bilirubin and inhibits an important enzyme complex called Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADPH) oxidase. By inhibiting NADPH oxidase, the phycocyanobilin in spirulina provides potent anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects.



 Protein
Protein
 Workout Support
Workout Support
 Build Muscle
Build Muscle
 Weight Loss
Weight Loss
 Protein Bars & Cookies
Protein Bars & Cookies
 Endurance
Endurance
 Wellness
Wellness